The Transformative Role of Emerging Technologies in the Modern World
In an age characterized by rapid technological advancement, emerging technologies are reshaping every facet of life—from how we communicate to how we work, learn, and entertain ourselves. As we stand on the cusp of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, it's essential to understand the key technologies driving these changes, their potential impacts, and the challenges they present.
1. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are at the forefront of technological innovation. These technologies enable machines to learn from data, make decisions, and even predict future trends. AI is already powering voice assistants like Siri and Alexa, automating customer service with chatbots, and optimizing supply chains in industries.
The potential applications of AI are vast. In healthcare, AI can analyze medical images faster and more accurately than human doctors, leading to quicker diagnoses and treatments. In finance, AI algorithms can detect fraudulent transactions in real-time, protecting both consumers and institutions. However, as AI continues to evolve, concerns about job displacement, ethical considerations, and the need for robust regulatory frameworks are becoming increasingly prominent.
2. Blockchain and Cryptocurrencies
Blockchain technology, initially developed as the underlying framework for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, has found applications far beyond digital currencies. A blockchain is a decentralized ledger that records transactions across many computers, making it nearly impossible to alter or hack the system. This technology is being used to improve transparency, security, and efficiency in various industries, from finance to supply chain management.
Cryptocurrencies have gained traction as an alternative to traditional financial systems, offering decentralized, peer-to-peer transactions. However, the volatility of cryptocurrencies and regulatory challenges pose significant hurdles to their widespread adoption. Despite these challenges, the potential for blockchain technology to revolutionize sectors such as voting systems, digital identity verification, and intellectual property rights remains substantial.
3. 5G and the Internet of Things (IoT)
The rollout of 5G technology is set to revolutionize the way we connect to the internet. With faster speeds, lower latency, and the ability to connect more devices simultaneously, 5G will be a critical enabler of the Internet of Things (IoT). IoT refers to the growing network of connected devices—ranging from smart home appliances to industrial sensors—that collect and share data in real-time.
In smart cities, IoT devices can monitor traffic patterns, reduce energy consumption, and improve public safety. In healthcare, wearable devices can track vital signs and alert doctors to potential health issues before they become critical. However, the proliferation of IoT devices also raises significant concerns about privacy, data security, and the potential for cyberattacks.
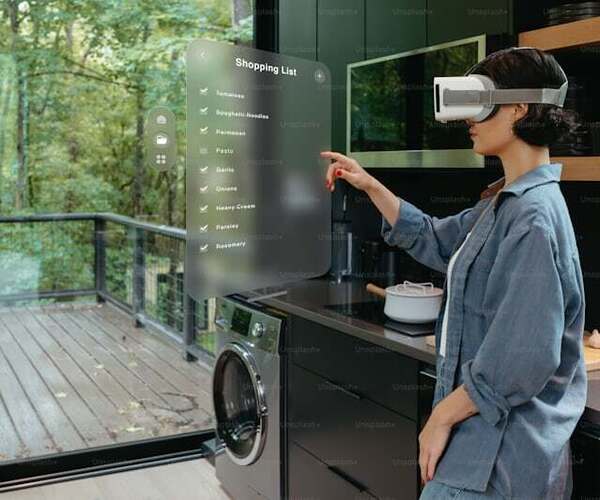
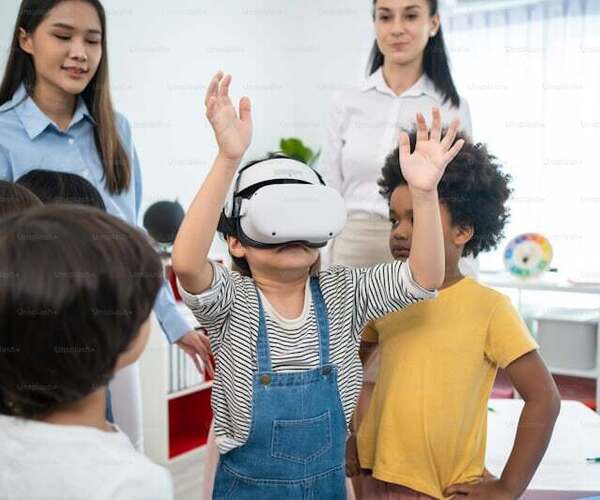
4. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) are transforming the way we interact with digital content. AR overlays digital information onto the real world, enhancing our perception of reality. This technology is already being used in applications ranging from navigation systems to educational tools. For instance, AR can enable surgeons to visualize a patient's anatomy before making an incision, improving the accuracy and outcomes of surgical procedures.
VR, on the other hand, immerses users in a fully digital environment, creating experiences that can be both entertaining and educational. The gaming industry has been one of the earliest adopters of VR, but its applications are expanding to include virtual meetings, training simulations, and even therapy for mental health conditions.
5. Quantum Computing
Quantum computing represents a leap forward in computational power, leveraging the principles of quantum mechanics to process information in ways that classical computers cannot. While still in its early stages, quantum computing has the potential to solve complex problems in fields like cryptography, materials science, and drug discovery, which are currently beyond the reach of conventional computers.
For instance, quantum computers could break modern encryption methods, leading to a new era of cybersecurity challenges. Conversely, they could also enable the creation of unbreakable encryption. The race to develop practical quantum computers is intensifying, with major tech companies and governments investing heavily in research and development.
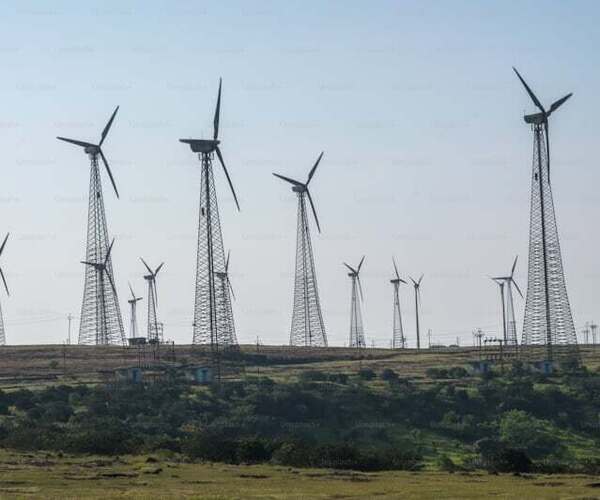
6. Sustainable Technologies
As the world grapples with climate change and environmental degradation, sustainable technologies are becoming increasingly critical. Innovations in renewable energy, such as solar and wind power, are reducing our reliance on fossil fuels. Advances in energy storage, like lithium-ion batteries and emerging solid-state batteries, are making it possible to store and use renewable energy more efficiently.
In agriculture, precision farming technologies are helping farmers optimize water usage, reduce chemical inputs, and increase crop yields. Sustainable technologies are also driving the development of electric vehicles, green buildings, and waste management solutions. However, the transition to a sustainable future requires not just technological innovation but also significant changes in policy, behavior, and investment.
Conclusion
The rapid advancement of these technologies offers incredible opportunities but also presents significant challenges. As AI, blockchain, 5G, IoT, AR, VR, quantum computing, and sustainable technologies continue to evolve, they will reshape industries, economies, and societies in profound ways. The key to harnessing their potential lies in responsible innovation, robust regulatory frameworks, and a commitment to addressing the ethical, social, and environmental implications of these emerging technologies.