The Role of Technology in Sustainable Development: Innovating for a Greener Future
Introduction: Sustainable development has become a global priority as we face the challenges of climate change, resource depletion, and environmental degradation. Technology plays a pivotal role in advancing sustainable development by offering innovative solutions that balance economic growth, social well-being, and environmental protection. From renewable energy and smart cities to circular economy practices and conservation technologies, the intersection of technology and sustainability is paving the way for a greener future. This article explores how technology is driving sustainable development across various sectors and its potential to create a more resilient and equitable world.
1. Renewable Energy: Powering the Future Sustainably
The transition from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources is crucial for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating climate change. Technological advancements have made renewable energy more efficient, affordable, and accessible.
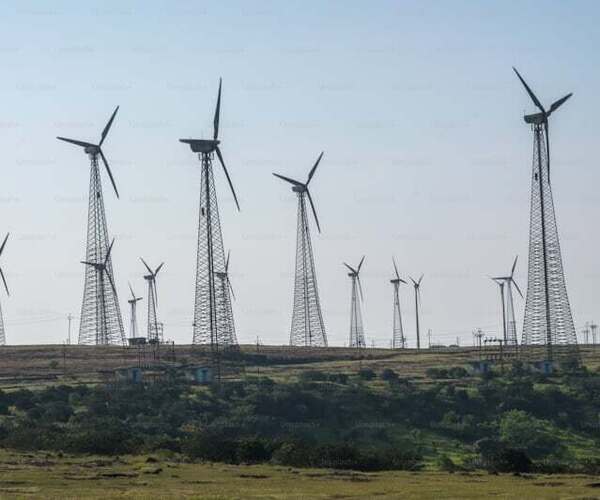
Solar and Wind Power: Solar and wind energy are at the forefront of the renewable energy revolution. Improvements in photovoltaic (PV) technology have significantly increased the efficiency of solar panels, while innovations in wind turbine design have made wind energy more cost-effective. These technologies are rapidly expanding, with large-scale solar farms and wind farms being developed worldwide to provide clean energy.
Energy Storage: One of the challenges of renewable energy is its intermittency, as solar and wind power depend on weather conditions. Advances in energy storage technologies, such as lithium-ion batteries and emerging solutions like solid-state batteries, are addressing this issue by storing excess energy generated during peak production times for use when demand is high or generation is low. This ensures a stable and reliable supply of renewable energy.
Smart Grids: The integration of renewable energy into existing power grids is facilitated by smart grid technology. Smart grids use sensors, data analytics, and automation to optimize the distribution and consumption of electricity, reducing energy waste and enhancing grid reliability. This technology enables better management of energy resources, supporting the transition to a more sustainable energy system.
2. Smart Cities: Building Sustainable Urban Environments
As urbanization continues to accelerate, smart cities are emerging as a solution to the challenges of population growth, resource management, and environmental impact. Technology is central to the development of smart cities, which aim to improve the quality of life for residents while minimizing environmental footprints.
IoT and Urban Infrastructure: The Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming urban infrastructure by connecting devices, sensors, and systems to create a more efficient and responsive city environment. Smart lighting, waste management, and water systems reduce resource consumption and operational costs, while real-time data collection and analysis enable city planners to make informed decisions about urban development.
Sustainable Transportation: Smart cities prioritize sustainable transportation options to reduce carbon emissions and improve air quality. Electric vehicles (EVs), public transit systems, and bike-sharing programs are integrated into the urban fabric, supported by smart traffic management systems that optimize traffic flow and reduce congestion. Autonomous vehicles and smart mobility solutions are also being explored to further enhance the efficiency of urban transportation.
Green Buildings: Technology is driving the construction of green buildings that are energy-efficient, resource-conscious, and environmentally friendly. Innovations in materials, such as recycled and sustainable building materials, combined with smart building systems that control lighting, heating, and cooling, contribute to reduced energy consumption and lower carbon footprints. Green building certifications, such as LEED, promote the adoption of sustainable practices in the construction industry.
3. Circular Economy: Rethinking Waste and Resource Management
The concept of the circular economy challenges the traditional linear model of production and consumption, where resources are extracted, used, and discarded. Instead, the circular economy promotes the continuous use of resources through recycling, reuse, and regeneration. Technology is key to enabling and scaling circular economy practices.
Waste Management Technologies: Innovations in waste management are crucial for achieving circular economy goals. Advanced recycling technologies, such as chemical recycling, can break down plastics into their original components for reuse, reducing the need for virgin materials. Additionally, waste-to-energy technologies convert non-recyclable waste into usable energy, minimizing landfill waste and generating clean power.
Product Lifecycle Management: Digital technologies, such as blockchain and IoT, are being used to track the lifecycle of products from production to disposal. This transparency enables better resource management, as companies can monitor the sustainability of their supply chains, optimize resource use, and encourage the recycling or repurposing of products at the end of their life.
Sustainable Product Design: Technology is driving innovation in product design, focusing on creating products that are durable, repairable, and recyclable. 3D printing, for example, allows for the creation of products with less material waste, and modular design enables easy repair and upgrading, extending the lifespan of products and reducing waste.
4. Conservation Technologies: Protecting Biodiversity and Ecosystems
The preservation of biodiversity and ecosystems is critical for maintaining the health of the planet. Technology is playing a vital role in conservation efforts by enabling better monitoring, protection, and restoration of natural environments.
Remote Sensing and Drones: Remote sensing technologies, including satellites and drones, are revolutionizing how we monitor ecosystems and wildlife. These tools provide real-time data on deforestation, habitat loss, and wildlife populations, allowing for timely interventions and informed conservation strategies. Drones are also used for reforestation efforts, where they can plant trees in areas that are difficult to access by traditional means.
AI and Machine Learning in Conservation: AI and machine learning are being used to analyze large datasets from conservation projects, helping to identify patterns and predict future trends. For example, AI can be used to track and predict the movement of endangered species, aiding in the development of targeted conservation efforts. These technologies also assist in identifying illegal activities, such as poaching and logging, by analyzing data from camera traps and other monitoring devices.
Marine Conservation Technologies: The health of marine ecosystems is vital for global biodiversity and climate regulation. Technology is helping to protect marine environments through innovations such as autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) that monitor coral reefs, track marine species, and detect pollution. Additionally, artificial intelligence is being used to analyze acoustic data to monitor marine life and detect illegal fishing activities.
5. The Future of Agriculture: Technology-Driven Sustainability
Agriculture is at the heart of sustainable development, as it directly impacts food security, livelihoods, and environmental health. Technological innovations are transforming agriculture, making it more productive, resilient, and sustainable.
Precision Agriculture: Precision agriculture uses GPS, IoT, and data analytics to optimize farming practices. By analyzing data on soil conditions, weather patterns, and crop health, farmers can apply inputs such as water, fertilizers, and pesticides more efficiently, reducing waste and environmental impact. Drones and sensors are also used to monitor crop growth and detect issues early, improving yields and reducing the need for chemical interventions.
Vertical Farming and Hydroponics: Vertical farming and hydroponic systems are revolutionizing food production by growing crops in controlled environments using minimal land and water. These technologies enable year-round production, reduce transportation costs by localizing food production, and significantly reduce the environmental footprint of agriculture.
Gene Editing and Sustainable Crops: Advances in biotechnology, particularly gene editing techniques like CRISPR, are being used to develop crops that are more resistant to pests, diseases, and climate change. These innovations can increase agricultural productivity while reducing the need for chemical inputs and water, contributing to more sustainable food systems.
6. The Role of Policy and Innovation in Sustainable Technology Adoption
The widespread adoption of sustainable technologies requires supportive policies and innovation ecosystems that encourage investment, research, and collaboration.
Government Incentives and Regulations: Governments play a critical role in promoting sustainable development through policies that incentivize the adoption of green technologies. Subsidies for renewable energy, tax breaks for sustainable practices, and regulations that limit emissions and resource use are essential for driving the transition to a sustainable economy.
Public-Private Partnerships: Collaboration between the public and private sectors is crucial for advancing sustainable technologies. Public-private partnerships can support research and development, scale-up innovative solutions, and ensure that sustainability initiatives are economically viable and socially inclusive.
Education and Awareness: Raising awareness about the importance of sustainability and the role of technology is key to driving change. Educational initiatives that promote environmental stewardship, innovation, and sustainable practices can empower individuals and communities to adopt and support sustainable technologies.
Conclusion: Technology is a powerful force for sustainable development, offering innovative solutions to some of the world’s most pressing challenges. From renewable energy and smart cities to circular economy practices and conservation technologies, the integration of technology into sustainability efforts is essential for creating a greener, more resilient future. However, the successful implementation of these technologies requires supportive policies, collaboration, and a commitment to addressing the social and environmental impacts of technological innovation. As we continue to advance, the intersection of technology and sustainability will be key to achieving a balanced and equitable world where both people and the planet can thrive.